- Home
- 8 Parts of Speech
8 Parts of Speech
The 8 parts of speech in English are: Nouns, Adjectives, Adverbs, Verbs, Prepositions, Pronouns, Conjunctions, and Interjections.
A part of speech is a category of words that have similar grammatical functions or properties. In other words, they play similar roles in a sentence. For instance, a verb shows the action of a subject or the subject's state of being.
We'll now look in more detail at the function of each of these parts of speech.
Understanding the 8 Parts of Speech
Nouns
Nouns are words used to talk about people, places, things, or ideas/concepts. Here are some examples:
- Person: The President
- Place: London
- Thing: Table
- Idea/concept: Neo-liberalism
So it may be naming something we can touch (e.g. table; book; car) or something we cannot touch (e.g. Neo-liberalism; happiness; wish).
There are both common nouns, used for classes of people, places, things, or ideas/concepts, and proper nouns, which is their given name, always with a capital letter.
Common Nouns
- man
- country
- shop
- political party
- street
Proper Nouns
- John
- Mumbai
- Tescos
- Democrats
- Chester Avenue
Learn more about the various types of noun >>
Adjectives
Another of the 8 parts of speech are adjectives. They describe nouns or pronouns. They can come before or after the noun/pronoun they describe:
Absolute Adjectives
- The large shopping complex
- The excited child
- She is happy
- It was a shocking film
- Her dress was lovely
- He's a good-looking man
These are absolute adjectives, but they can also be comparative (comparing two or more things) or superlative (showing degree or quality):
Comparative Adjectives
- She's fitter than the others
- Their house is bigger
- I ran faster than you
- Cats are more agile than dogs
- Sue's more tired than Tim
Superlative Adjectives
- She's the fittest
- Their house is the biggest
- I ran the fastest
- Cats are the most agile
- Sue's the most tired
There are various other types of adjective. Learn more about the different types of adjectives >>
Adverbs
Adverbs modify verbs, other adverbs, and adjectives. There are adverbs of manner, time, place and degree. Here are examples of each being modified in relation to verbs, adverbs, and adjectives (the word being modified is underlined):
Adverbs Modifying Verbs
- He runs fast
- Ian quickly left the room
- She spoke slowly
Adverbs Modifying Other Adverbs
- He runs exceptionally fast
- Ian very quickly left the room
- She spoke extremely slowly
Adverbs Modifying Adjectives
- She's really excited
- He's happily married
- The elegantly designed dress is mine
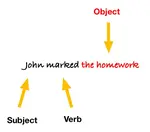
Verbs
Verbs form part of the predicate of a sentence.
In relation to the subject, they are used to express a physical action (e.g. walk; speak; show) or a mental action (e.g. think; feel; want). They can also express a state of being, mainly with the verb 'to be' but also some others.
Here are some examples:
Physical Action
- He ran home
- They chose the blue one
- She spoke slowly
Mental Activity
- I am thinking about it
- Ian guessed the answer
- She believes in ghosts
State of Being
- She is a police woman
- I am tired
- They seem worried
These though are main verbs. They have many other uses in a sentence so you should read about all the types of verbs further.
Prepositions
Another of the 8 parts of speech are prepositions. These show the relationship between two words or phrases in a sentence. They precede a noun or pronoun.
Commons examples of prepositions are above, up, upon, at, before, behind, since, to, through, under, until, with, within, about, against, along, around, beside, between, down, during, below, by, except, for, from, in, into, like, near, of, off, on, toward.
In these example sentences with prepositions, the two words whose relationship is being expressed are underlined and the prepositions are in bold:
- The book is on the table
- He is the leader of the conservative party
- The boy picked up the toy under the sofa
- This is a present for your mother
Pronouns
Pronouns replace nouns and they prevent us from repeating the noun in a sentence. These are the types of pronouns with some examples:
- Personal e.g. I; you; they; she
- Possessive e.g. mine; yours; his; theirs
- Relative e.g. who; which; that; whom
- Demonstrative e.g. this; these; those
- Reciprocal e.g. one another; each other
- Emphatic / Reflexive e.g. myself; herself; itself; ourselves
- Interrogative e.g. what; which; whom; whose
Here are some examples of these words used in sentences:
- Martha decided she would leave
- Why don't you use his car instead of mine
- Mick is a person who learns quickly
- Shall we buy some of these?
- They began to argue with each other
- Jenny is pleased with herself
- What time is he coming?
Conjunctions
Conjunctions are the of the 8 parts of speech responsible for joining together words, phrases, or clauses. There are three types:
- Coordinating: and; or; but; so; yet; for; nor
- Correlative: neither/nor; either/or; not only/but also
- Subordinating: e.g. although; because; while; which; where; until
Coordinating Conjunctions
Used to connect like for like words (e.g. noun+noun):
- I like apples and oranges (2 nouns)
- His speech was slow but effective (2 adjectives)
- Shall I say it loudly or quietly? (2 adverbs)
Or simple sentences (independent clauses):
- I find the music annoying but she finds It pleasant
- She came to the lecture late so she missed everything important
- She took her umbrella for it was raining hard
Correlative Conjunctions
Used to join alternative or equal elements:
- He felt neither happy nor sad about it
- Sue had to decide to either quit or carry on
- I went not only to Australia but also to New Zealand
Subordinating Conjunctions
Used to join subordinate clauses to main clauses:
- The government won't vote on the bill until both parties agree
- I'm still not tired although it is late
- I'll eat the dish which you don't like
Interjections
Interjections are words used to express an emotion or a sentiment such as surprise, joy, disgust, fear, excitement, pain, or enthusiasm.
They usually appear at the start of a sentence and are not connected to it grammatically. Here are some examples of interjections in sentences:
- Wow, that's an amazing score!
- Oh, I didn't know you failed the exam
- Well, we better not leave too late
- Ow, that really hurt!
- Ah, I understand now
- Oops, I've forgotten to bring the sandwiches
Learn more about interjections >>
Are there only 8 Parts of Speech?
Sometimes rather than 8 parts of speech, you may see 9 or 10 listed. This is because some people treat articles and determiners as separate categories.
However, when there are only 8 parts of speech considered (as above), this is because as these two types of word modify nouns, they are classified under adjectives.
Now practice what you have learned in our identifying parts of speech quiz
New! Comments
Any questions or comments about the grammar discussed on this page?
Post your comment here.