Present Simple Tense
The present simple tense varies according to whether it is being used with a third person singular subject or other subjects.
In this lesson we will look at:
- Forming the Present Simple (3rd person; other verbs; to be;)
- When to use the Present Simple
Forms of the Present Simple Tense
It is important to be aware of the third person singular (he/she/it) and other subjects (you/we/they) when forming the present simple because the form of the tense varies according to this:
- First-person singular: I see
- Second-person singular: You see
- Third-person singular: He/she/it sees
- First-person plural: We see
- Second-person plural: You see
- Third-person plural: They see
The formation of the tense will also vary according to whether you are using the affirmative, negative, or a question.
Present Simple with 3rd Person Singular Subjects
The 3rd person singular refers to the following subjects:
- he (John, Ian etc)
- she (Anne, Susan etc)
- it (the book, the film etc)
The present simple tense table below shows you how the formation will vary according to the affirmative, negative, or a question. You'll see we need to add an '-s' to the verb for affirmative statements, but we add in does / doesn't (auxiliary verbs) for negative statements and questions.
Note that questions can either be yes / no questions or have questions words. For example:
- Q: Do you like to holiday abroad?
- A: Yes / No
- Q: Where do you like to go on holiday?
- A: Spain
3rd Person Verb Endings
For many 3rd person verbs in the present simple tense, we add '-s':
- laugh = laughs
- work = works
- cope = copes
- love = loves
However, typically if the verb ends in o, ss, sh, ch, x or z, we add '-es'
- go = goes
- loss = losses
- wish = wishes
- catch = catches
- tax = taxes
- fizz = fizzes
For verbs ending in a consonant plus -y, the -y is replaced with an i, then -es is added.
- hurry = hurries
- bury = buries
- try = tries
- clarify = clarifies
Who
It should be noted at this point that with the question word 'who' in the present simple tense, we often do not use auxiliary verbs:
- Who likes vegetarian food? (not "Who does like...")
- Who takes ibuprofen? (not "Who does take...")
Other Subjects
For the other subjects in the present simple tense (i.e. I, you, we, they), no '-s' is added to the verb, and we use do or don't for negative statements and questions.
Present Simple 'to be'
The verb to be follows a different pattern to other types of verbs. We still use the '-s' for third person singular (is) but we do not use do / does - rather we use is / am / are:
- First-person singular: I am
- Second-person singular: You are
- Third-person singular: He/she/it is
- First-person plural: We are
- Second-person plural: You are
- Third-person plural: They are
Download Present Simple Form Tables
It should be noted that it is accepted to use 'aren't I' rather than 'am not I', even though this does not fit the grammar rules.
- Why aren't I invited?
- I'm going to get in trouble, aren't I?
When do we use the Present Simple Tense?
Repeated Events
A common use of the present simple tense is to describe repeated events, or what we also refer to as habits and routines. It's quite common to use adverbs of frequency (e.g. always, often, usually etc) and expressions of repeated time (e.g. on Mondays, in the winter, every month) for habitual behaviour.
Examples of repeated events (habits and routines):
- I get up early
- Why don't you eat fish?
- I practice the piano everyday
- I always travel during my holidays
- She works from Mondays to Wednesdays
- Where do they usually meet?
General Facts
We also use the present simple tense for general facts, or things that are always true (or at least true at the time the fact is given).
Examples of general facts:
- Fresh water freezes at 32 degrees fahrenheit
- She likes the colour pink
- I live in Paris
- Elephants are the only animals that can't jump
- Owning a gun isn't illegal in the US
- 2 + 2 equals 4
State Verbs
The present simple tense is used to talk about states, or in other words with stative verbs. This is because we do not tend to use these verbs with the present continuous tense.
For instance, we can't say "I am having a headache". We say "I have a headache".
Examples of state verbs:
- Existence: I am alive; She exists
- Wants and Likes: I like you; They want a pay rise
- Possession: I have many handbags; John owns a car
- Mental States: I believe in ghosts; I understand
- Senses: I feel unwell; It smells strange
- Appearance: You look tired; She seems ok
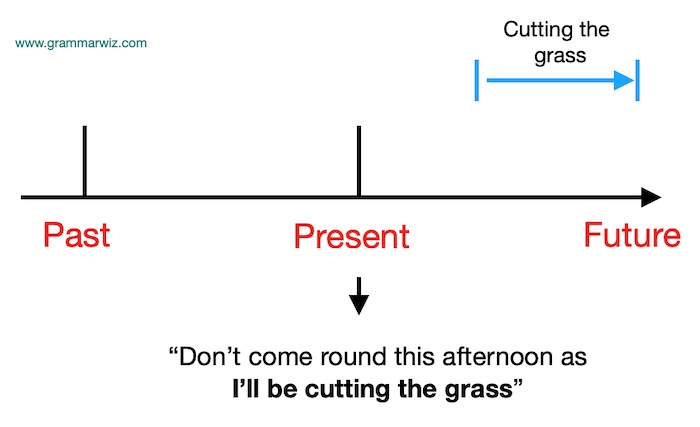
Talking about the future
We can also use the present simple tense to talk about the future, either the fixed future, using phrases such as next week, tomorrow, at 5pm, or after time words (e.g. when, before, after) and after if and unless.
Fixed time:
- The train leaves at 6.45pm
- Shall we go to the cinema tonight?
- My new job starts next week
- She arrives tomorrow
Time words:
- I'll tell you when she makes a decision
- Make sure you've cleaned your teeth before you go to bed
- I'm going to start making dinner after they arrive
If and unless:
- If he passes his exam, he'll be very happy
- I won't help you unless you listen to me
Stories in the past
Though we usually use past tenses for stories or narratives about the past, very occasionally we use the present simple.
This is usually to tell a comic story or dramatic story, and using the present simple tense gives the story a sense of immediacy (making the person listening feel like they are there) or excitement.
Past narrative:
A strange thing happened to me yesterday. So I was in town and this man comes up to me and asks me the time. He then tells me he really needs help as some people are after him. I look around though and don't see anyone, but then suddenly he runs off. I don't know what it was all about.
Now practice or test yourself in this online Present Simple Quiz
New! Comments
Any questions or comments about the grammar discussed on this page?
Post your comment here.